【reverse】虚假控制流入门:Ubuntu20.04安装ollvm4.0踩坑记+用IDApython去除BCF
破解资源 发布日期:2025/1/10 浏览次数:1
引言
虚假控制流(Bogus Control Flow,BCF),通过加入包含不透明谓词的条件跳转(也就是跳转与否在运行之前就已经确定的跳转,但IDA无法分析)和不可达的基本块,来干扰IDA的控制流分析和F5反汇编。
依赖
- IDA7.7
- 虚拟机Ubuntu20.04
Ubuntu20.04安装ollvm+各种踩坑记录
根据参考链接1,主要的命令就这些:
# 截至2022.09.25,这玩意已经5年没更新了……git clone -b llvm-4.0 https://github.com/obfuscator-llvm/obfuscator.git# 这里build文件夹和obfuscator-llvm-4.0文件夹同级mkdir build-llvm-4.0 && sudo chmod 777 -R build-llvm-4.0 && cd build-llvm-4.0cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release ../obfuscator-llvm-4.0/# 防止出现Permission Deniedsudo make -j5但你先别急,这里水很深,不看完参考链接1以及我总结的踩坑记录的话,泥巴握不住!
作者:hans774882968以及hans774882968以及hans774882968
本文52pojie:https://www.52pojie.cn/thread-1692596-1-1.html
本文juejin:https://juejin.cn/post/7147302252846252046/
本文csdn:https://blog.csdn.net/hans774882968/article/details/127043163
1、gcc和g++需要降级
如果用的是9及以后的版本,make时会没有任何提示,忽然报错make: *** [Makefile:152:all] 错误 2。直接执行下面这些命令进行降级就行:
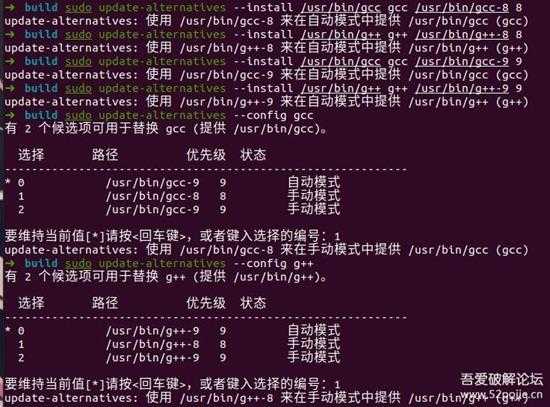
sudo apt install gcc-8 g++-8 -ysudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/gcc gcc /usr/bin/gcc-8 8sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/g++ g++ /usr/bin/g++-8 8sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/gcc gcc /usr/bin/gcc-9 9sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/g++ g++ /usr/bin/g++-9 9sudo update-alternatives --config gccsudo update-alternatives --config g++# 最后可以看看版本是否修改成功gcc -vg++ -v效果
1.jpg
2、编译前要先修改源码
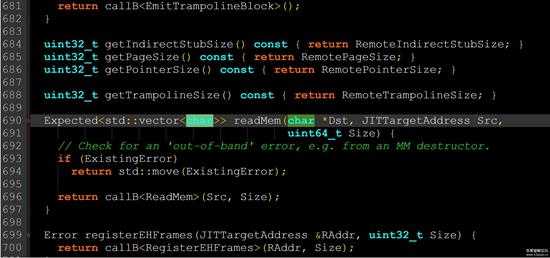
根据参考链接1,不修改源码会踩坑。找到<你的ollvm目录>/include/llvm/ExecutionEngine/Orc/OrcRemoteTargetClient.h,按照下图把690行的readMem的返回类型从Expected<vector<char改为Expected<vector<uint8_t(这里参考链接1错误地说成了uint_8了)。
2.jpg
3、注意权限问题
如果你在编译时,看到make失败前有一大堆Permission Denied,说明你权限没给够。
- 建议编译前给到
build-llvm-4.0和obfuscator-llvm-4.0的父文件夹777权限:sudo chmod 777 -R <父文件夹名>,防止新生成的文件Permission Denied。 - 不要在挂载点的文件夹进行编译,否则会有权限错误。
- 建议编译期间每次看到
build-llvm-4.0/bin新生成一个文件,都给它777权限,防止Permission Denied造成失败(其实编译失败也没事,编译好的文件不会重新编译,不是很耽误时间。每次看到新生成的文件出现Permission Denied,先给它权限再重新编译即可)。
4、给足虚拟机内存
不给足内存的话虚拟机会死机。也可以选择降一降作业数,比如sudo make -j7降到sudo make -j5。
编译成功
大概等了一小时,终于成功了!纪念一下!
3-终于make成功了,纪念一下.jpg
先看一个demo
写个bcf_demo.cpp:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;#define rep(i,a,b) for(int i = (a);i <= (b);++i)#define re_(i,a,b) for(int i = (a);i < (b);++i)#define dwn(i,a,b) for(int i = (a);i >= (b);--i)void dbg() { puts ("");}template<typename T, typename... R>void dbg (const T &f, const R &... r) { cout << f << " "; dbg (r...);}template<typename Type>inline void read (Type &xx) { Type f = 1; char ch; xx = 0; for (ch = getchar(); ch < '0' || ch > '9'; ch = getchar() ) if (ch == '-') f = -1; for (; ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'; ch = getchar() ) xx = xx * 10 + ch - '0'; xx *= f;}void read() {}template<typename T, typename ...R>void read (T &x, R &...r) { read (x); read (r...);}int main (int argc, char const *argv[]) { char name[100]; scanf ("%s", name); if (strcmp (name, "Alice") == 0) { printf ("hello, %s.\n", name) ; } else if (strcmp (name, "Bob") == 0) { printf ("hello, %s\n", name); } else { printf ("no permission.\n"); } return 0;}用clang正常编译
'build-llvm-4.0/bin/clang++ 的绝对路径' 'bcf_demo.cpp 的绝对路径' -o bcf_demo_normalIDA反汇编效果:
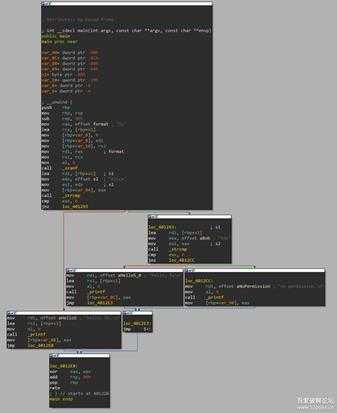
int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp){ char s1[112]; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-80h] BYREF const char **v5; // [rsp+80h] [rbp-10h] int v6; // [rsp+88h] [rbp-8h] int v7; // [rsp+8Ch] [rbp-4h] v7 = 0; v6 = argc; v5 = argv; scanf("%s", s1); if ( !strcmp(s1, (const char *)(unsigned int)"Alice") ) { printf("hello, %s.\n", s1); } else if ( !strcmp(s1, (const char *)(unsigned int)"Bob") ) { printf("hello, %s\n", s1); } else { printf("no permission.\n"); } return 0;}流程图:
4.jpg
加上bcf,编译:
'build-llvm-4.0/bin/clang++ 的绝对路径' -mllvm -bcf 'bcf_demo.cpp 的绝对路径' -o bcf_demoIDA反汇编效果:
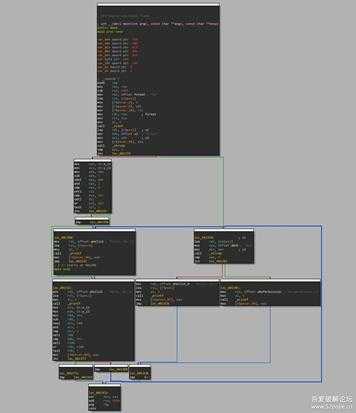
int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp){ char s1[112]; // [rsp+20h] [rbp-80h] BYREF const char **v5; // [rsp+90h] [rbp-10h] int v6; // [rsp+98h] [rbp-8h] int v7; // [rsp+9Ch] [rbp-4h] v7 = 0; v6 = argc; v5 = argv; scanf("%s", s1); if ( !strcmp(s1, (const char *)(unsigned int)"Alice") ) { if ( y_12 >= 10 && ((((_BYTE)x_11 - 1) * (_BYTE)x_11) & 1) != 0 ) goto LABEL_9; while ( 1 ) { printf("hello, %s.\n", s1); if ( y_12 < 10 || ((((_BYTE)x_11 - 1) * (_BYTE)x_11) & 1) == 0 ) break;LABEL_9: printf("hello, %s.\n", s1); } } else if ( !strcmp(s1, (const char *)(unsigned int)"Bob") ) { printf("hello, %s\n", s1); } else { printf("no permission.\n"); } return 0;}流程图:
5.jpg
对比两图,bcf确实让程序更复杂了。
这些跳转中的x_11和y_12位于.bss段,并且通过交叉引用发现没有被修改过,也就是说x_11和y_12在运行过程中一直为0。这里的x_11和y_12被称为不透明谓词,所谓不透明,就是IDA难以推断其在运行时的值,但我们都知道它就是0。
简单分析一下bcf加入的干扰语句。y_12 >= 10 && ((((_BYTE)x_11 - 1) * (_BYTE)x_11) & 1) != 0:因为相邻两个数的乘积必为偶数,故此式总是false。根据德摩根定律,y_12 < 10 || ((((_BYTE)x_11 - 1) * (_BYTE)x_11) & 1) == 0就总是true。因此printf("hello, %s.\n", s1);恰好只执行一次。那些永远不会执行到的代码块,就叫做不可达的基本块。这些跳转和不可达基本块并不会影响程序原有的逻辑,但会干扰我们的分析,这就是虚假控制流混淆达到的效果。
尝试用IDApython去除bcf
我们把上面的demo写得更复杂一点:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;#define rep(i,a,b) for(int i = (a);i <= (b);++i)#define re_(i,a,b) for(int i = (a);i < (b);++i)#define dwn(i,a,b) for(int i = (a);i >= (b);--i)void dbg() { puts ("");}template<typename T, typename... R>void dbg (const T &f, const R &... r) { cout << f << " "; dbg (r...);}template<typename Type>inline void read (Type &xx) { Type f = 1; char ch; xx = 0; for (ch = getchar(); ch < '0' || ch > '9'; ch = getchar() ) if (ch == '-') f = -1; for (; ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'; ch = getchar() ) xx = xx * 10 + ch - '0'; xx *= f;}void read() {}template<typename T, typename ...R>void read (T &x, R &...r) { read (x); read (r...);}int main (int argc, char const *argv[]) { char name[100]; scanf ("%s", name); if (strcmp (name, "Alice") == 0) { printf ("hello, %s.\n", name) ; } else if (strcmp (name, "Bob") == 0) { printf ("hello, %s\n", name); } else { printf ("no permission.\n") ; return 0; } re_ (i, 0, 10) { if (i & 1) dbg (i << 1); else dbg (i << 1 | 1); } return 0;}加上bcf编译,用IDA看看patch前的效果:
int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp){ int v4; // [rsp+24h] [rbp-8Ch] BYREF int v5; // [rsp+28h] [rbp-88h] BYREF int i; // [rsp+2Ch] [rbp-84h] char s1[112]; // [rsp+30h] [rbp-80h] BYREF const char **v8; // [rsp+A0h] [rbp-10h] int v9; // [rsp+A8h] [rbp-8h] int v10; // [rsp+ACh] [rbp-4h] v10 = 0; v9 = argc; v8 = argv; scanf("%s", s1); if ( !strcmp(s1, (const char *)(unsigned int)"Alice") ) { printf("hello, %s.\n", s1); } else { if ( strcmp(s1, (const char *)(unsigned int)"Bob") ) { if ( y_13 >= 10 && ((((_BYTE)x_12 - 1) * (_BYTE)x_12) & 1) != 0 ) goto LABEL_18; while ( 1 ) { printf("no permission.\n"); v10 = 0; if ( y_13 < 10 || ((((_BYTE)x_12 - 1) * (_BYTE)x_12) & 1) == 0 ) return v10;LABEL_18: printf("no permission.\n"); v10 = 0; } } printf("hello, %s\n", s1); } for ( i = 0; ; ++i ) { while ( y_13 >= 10 && ((((_BYTE)x_12 - 1) * (_BYTE)x_12) & 1) != 0 ) ; if ( i >= 10 ) break; if ( (i & 1) != 0 ) { v5 = 2 * i; dbg<int>(&v5); continue; } if ( y_13 >= 10 && ((((_BYTE)x_12 - 1) * (_BYTE)x_12) & 1) != 0 ) {LABEL_20: v4 = (2 * i) | 1; dbg<int>(&v4); } v4 = (2 * i) | 1; dbg<int>(&v4); if ( y_13 >= 10 && ((((_BYTE)x_12 - 1) * (_BYTE)x_12) & 1) != 0 ) goto LABEL_20; } return 0;}我们随便找个例子,看看干扰代码的汇编长什么样:
.text:000000000040151C 8B 04 25 B4 41 40 00 mov eax, ds:x_12.text:0000000000401523 8B 0C 25 9C 41 40 00 mov ecx, ds:y_13.text:000000000040152A 89 C2 mov edx, eax.text:000000000040152C 83 EA 01 sub edx, 1.text:000000000040152F 0F AF C2 imul eax, edx.text:0000000000401532 83 E0 01 and eax, 1.text:0000000000401535 83 F8 00 cmp eax, 0.text:0000000000401538 40 0F 94 C6 setz sil.text:000000000040153C 83 F9 0A cmp ecx, 0Ah.text:000000000040153F 40 0F 9C C7 setl dil.text:0000000000401543 40 08 FE or sil, dil.text:0000000000401546 40 F6 C6 01 test sil, 1.text:000000000040154A 0F 85 05 00 00 00 jnz loc_401555.text:000000000040154A.text:0000000000401550 E9 F3 01 00 00 jmp loc_401748我们不需要管这些干扰指令具体是true还是false,只需要知道:它们不影响原有代码。我们简单分析可知,这里的jnz loc_401555一定会执行,因此我们只需要把jnz loc_401555改成jmp loc_401555,即可去除所有的干扰效果。
IDApython脚本:
import idcdef next_instr(addr): # item_size返回addr处指令长度 return addr + idc.get_item_size(addr)def main(): print('-' * 40) st_addr = 0x401470 ed_addr = 0x401793 addr = st_addr while addr < ed_addr: next = next_instr(addr) if 'x_12' in idc.GetDisasm(addr): # 向下找到jnz while addr < ed_addr and 'jnz' not in idc.GetDisasm(addr): addr = next next = next_instr(addr) if addr >= ed_addr: break print(idc.GetDisasm(addr)) # dbg # 获取jnz跳转的目的地址 dest = idc.get_operand_value(addr, 0) print('dest', hex(dest)) # dbg # 将jnz patch成jmp idc.patch_byte(addr, 0xE9) # 计算目的地址相对addr的偏移offset offset = dest - (addr + 5) # 将jmp操作数patch为offset idc.patch_dword(addr + 1, offset) # patch jnz指令最后一个字节为nop idc.patch_byte(addr + 5, 0x90) addr = next print('-' * 40)main()输出:
jnz loc_401555dest 0x401555jnz loc_4015ACdest 0x4015acjnz loc_4015F9dest 0x4015f9jnz loc_401642dest 0x401642jnz loc_4016C0dest 0x4016c0jnz loc_401717dest 0x401717在上述例子中,patch后,只有一条指令被修改了:
.text:000000000040151C 8B 04 25 B4 41 40 00 mov eax, ds:x_12.text:0000000000401523 8B 0C 25 9C 41 40 00 mov ecx, ds:y_13.text:000000000040152A 89 C2 mov edx, eax.text:000000000040152C 83 EA 01 sub edx, 1.text:000000000040152F 0F AF C2 imul eax, edx.text:0000000000401532 83 E0 01 and eax, 1.text:0000000000401535 83 F8 00 cmp eax, 0.text:0000000000401538 40 0F 94 C6 setz sil.text:000000000040153C 83 F9 0A cmp ecx, 0Ah.text:000000000040153F 40 0F 9C C7 setl dil.text:0000000000401543 40 08 FE or sil, dil.text:0000000000401546 40 F6 C6 01 test sil, 1.text:000000000040154A E9 06 00 00 00 jmp loc_401555.text:000000000040154A.text:000000000040154A ; ---------------------------------------------------------------------------.text:000000000040154F 90 db 90h.text:0000000000401550 E9 F3 01 00 00 jmp loc_401748patch后反汇编效果:
int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp){ int v4; // [rsp+24h] [rbp-8Ch] BYREF int v5; // [rsp+28h] [rbp-88h] BYREF int i; // [rsp+2Ch] [rbp-84h] char s1[112]; // [rsp+30h] [rbp-80h] BYREF const char **v8; // [rsp+A0h] [rbp-10h] int v9; // [rsp+A8h] [rbp-8h] int v10; // [rsp+ACh] [rbp-4h] v10 = 0; v9 = argc; v8 = argv; scanf("%s", s1); if ( !strcmp(s1, (const char *)(unsigned int)"Alice") ) { printf("hello, %s.\n", s1); } else { if ( strcmp(s1, (const char *)(unsigned int)"Bob") ) { printf("no permission.\n"); return 0; } printf("hello, %s\n", s1); } for ( i = 0; i < 10; ++i ) { if ( (i & 1) != 0 ) { v5 = 2 * i; dbg<int>(&v5); } else { v4 = (2 * i) | 1; dbg<int>(&v4); } } return 0;}效果不错,去得很干净。
地球人用angr去除bcf的做法以后(下辈子)再学。
参考资料
- Ubuntu20.04安装ollvm各种踩坑记录:https://www.bilibili.com/read/cv13148974/
- 地球人yyds%%%:https://bbs.pediy.com/thread-266005.htm